Barn Owl Food Chain Coloring Page Owl Food Food Web Food Chain Biology Diagrams
Barn Owl Food Chain Coloring Page Owl Food Food Web Food Chain Biology Diagrams The iconic barn owl, with its heart-shaped face, Introduced into the UK in the 19th century, the diminutive little owl can now be seen along hedgerows, on farmland, and in parkland across England and Wales. It often perches on a pole or rock, looking out for its unsuspecting prey. Apex predators - the role of owls in the food chain .
Ecological Benefits. Beyond direct pest control, owls play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of the farm's ecosystem. As predators, they help control small animal populations, which prevents overgrazing and resource depletion.Their presence also contributes to the natural food chain, with owls becoming prey for larger predators.This complex interaction helps maintain a

The Environmental Literacy Council Biology Diagrams
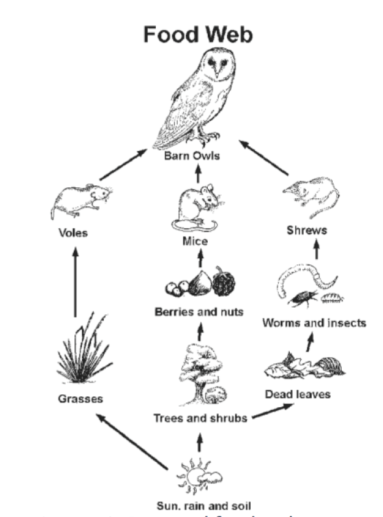
Barn Owls prefer a mixed farming habitat with spinneys, ditches, rough pastures and well-managed field margins. Grassland makes good hunting ground, along with hay meadows. They are often found around farm buildings, barns and the edge of villages. A breeding pair of barn owls needs around 1.5 ha of rough grass.. Food Barn Owls prefer a mixed farming habitat with spinneys, ditches, rough pastures and well-managed field margins. Grassland makes good hunting ground, along with hay meadows. They are often found around farm buildings, barns and the edge of villages. A breeding pair of barn owls needs around 1.5 ha of rough grass.. Food How much land? How to manage land for Barn Owls; Nesting & roosting; Environmental Land Management Schemes; Biodiversity Net Gain; Hazards & Solutions. Rat poison. Safer rat control; Major roads. High speed trains - HS2; Nest & roost site loss; Planning decisions; Barn Owl Food Chain. Facebook;
Barn Owls are birds of prey - specialised hunters at the top of the food chain, which means that they need to eat prey animals to survive. Prey animals - mainly small mammals - eat other smaller creatures or plants, seeds and fruits. The barn owl nests and roosts in tree cavities, old and derelict farm buildings. Nest boxes are also used by barn owls both in buildings and outside. The 4-6 eggs are incubated for 30 days. Young birds fly after 50 days but are dependent on the parents for food for a further 3-5 weeks. The decline of barn owl ### A family of barn owls, typically a breeding pair with offspring, can consume an estimated 3,400 to 7,000 rodents per year. The exact number depends on the number of owlets and the availability of prey. 2. What are the best habitats for barn owls on a farm? Barn owls prefer open habitats for hunting, making row crops ideal.
